TL;DR: We introduce OpenVO, a novel framework for Open-world Visual Odometry (VO) with temporal awareness under limited input conditions.
OpenVO effectively estimates real-world–scale ego-motion from monocular dashcam footage with varying observation rates and uncalibrated cameras, enabling robust trajectory dataset construction from rare driving events recorded in dashcam.
Existing VO methods are trained on fixed observation frequency (e.g., 10Hz or 12Hz), completely overlooking temporal dynamics information. Many prior methods also require calibrated cameras with known intrinsic parameters.
Consequently, their performance degrades when (1) deployed under unseen observation frequencies or (2) applied to uncalibrated cameras. These significantly limit their generalizability to many downstream tasks, such as extracting trajectories from dashcam footage.
To address these challenges, OpenVO (1) explicitly encodes temporal dynamics information within a two-frame pose regression framework and (2) leverages 3D geometric priors derived from foundation models. We validate our method on three major autonomous-driving benchmarks -- KITTI, nuScenes, and Argoverse 2 -- achieving more than 20% performance improvement over state-of-the-art approaches.
Under varying observation rate settings, our method is significantly more robust, achieving 46%–92% lower errors across all metrics.
These results demonstrate the versatility of OpenVO for real-world 3D reconstruction and diverse downstream applications.
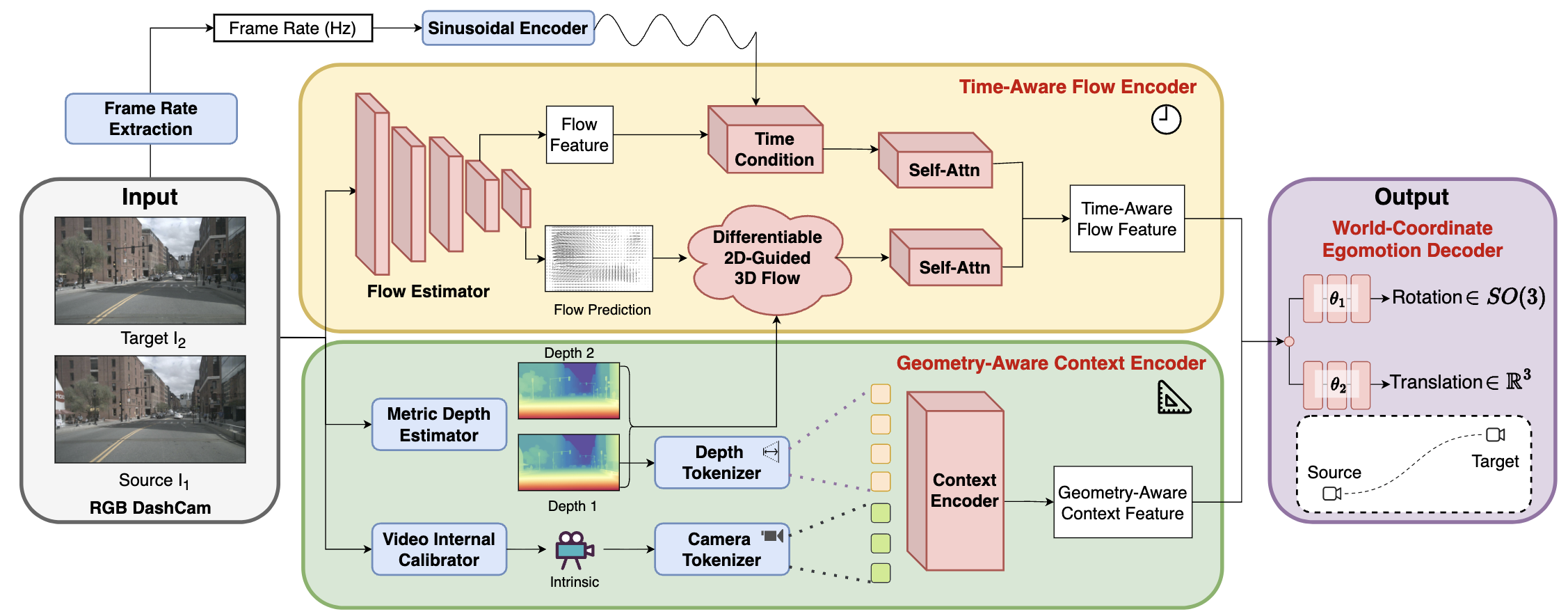
We propose a novel temporal-dynamics-informed, geometry-aware visual odometry system. Our method takes consecutive dashcam frames as input and extracts both temporal and geometric representations for robust egomotion estimation. The Time-Aware Flow Encoder leverages a Differentiable 2D-Guided 3D Flow module and time-conditioned embeddings to model motion dynamics across varying observation rates, while the Geometry-Aware Context Encode incorporates metric depth and intrinsic priors to build a consistent 3D geometry structure of the scene. Finally, the World-Coordinate Egomotion Decoder predicts accurate world-coordinate egomotion trajectories from the fused dynamic-geometric representation.
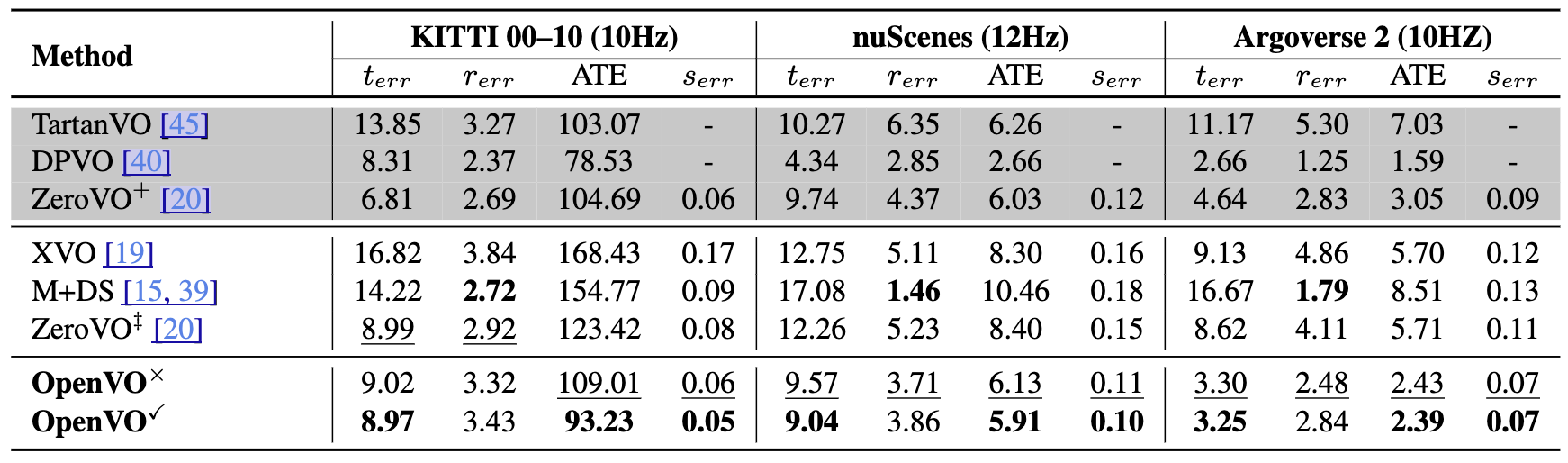
Generalizability results. Comparison with existing methods on three large-scale driving benchmarks using standard metrics: translation, rotation, absolute trajectory, and scale error. OpenVO is trained exclusively on nuScenes and evaluated on KITTI and Argoverse 2 with unseen camera setups, as well as unseen regions of nuScenes, to assess cross-domain generalization.
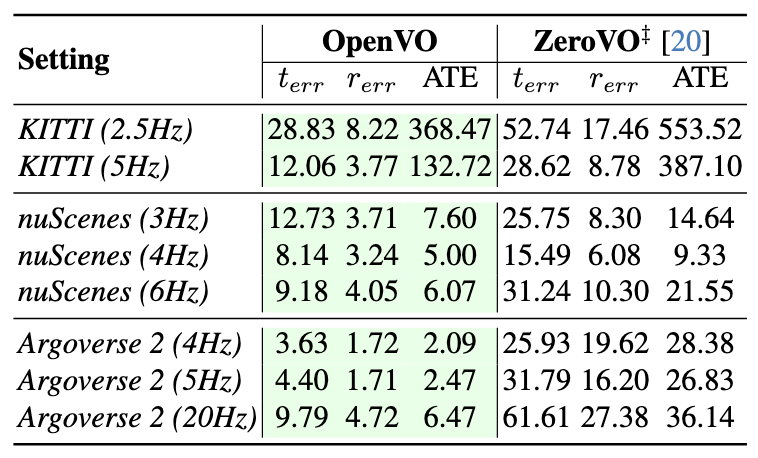
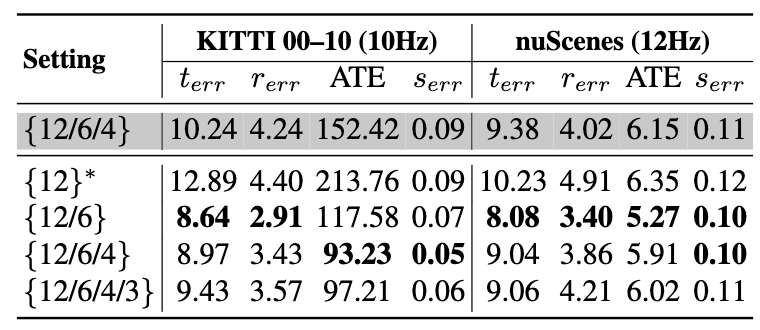
Left: Ablation on Varying Inference Observation Rates. ‡ indicates ZeroVO uses the same Metric Depth and Intrinsic priors from foundation models as OpenVO. Green cells denote OpenVO (left) improved performance of over existing method (right). Our OpenVO is significantly more robust to observation rate variations, consistently reducing VO errors by 46% to 92% across different metrics and benchmark settings.
Right: Ablation on Training Observation Frequency. Shaded row : OpenVO trained without proposed Time Condition Layers; Other rows : OpenVO trained with proposed Time Condition Layers. ∗ indicates that OpenVO uses 12 Hz as the fixed inference temporal condition, regardless of the dataset
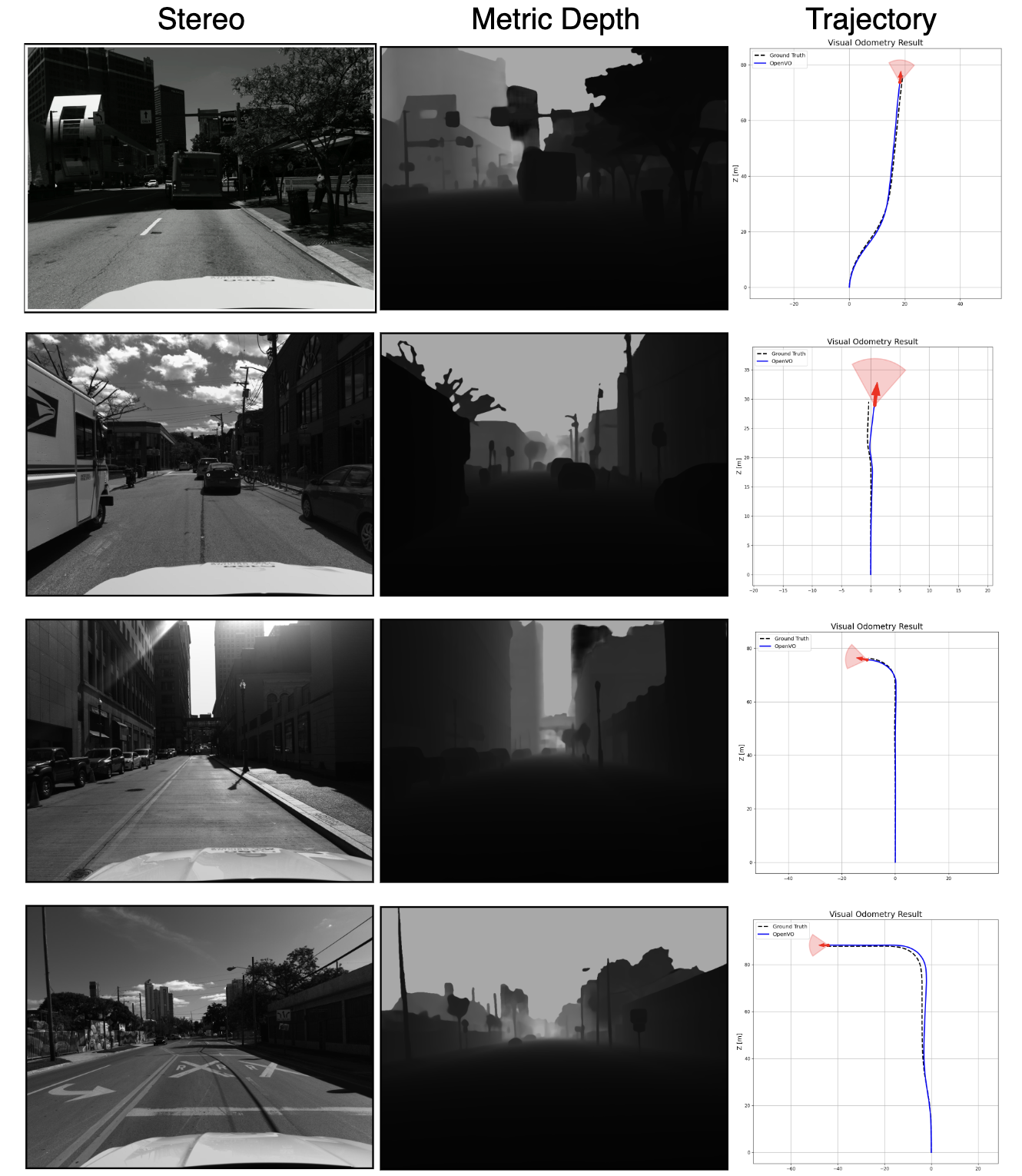
Qualitative of Stereo benchmark on Argoverse 2. Each row shows one example, including the input stereo image and the reference metric depth. The stereo images in Argoverse 2 often provides low-quality or weakly constrained metric depth due to limited disparity in long-range regions and visually challenging street scenes. This degradation leads to information loss and introduces uncertainty into downstream VO estimation
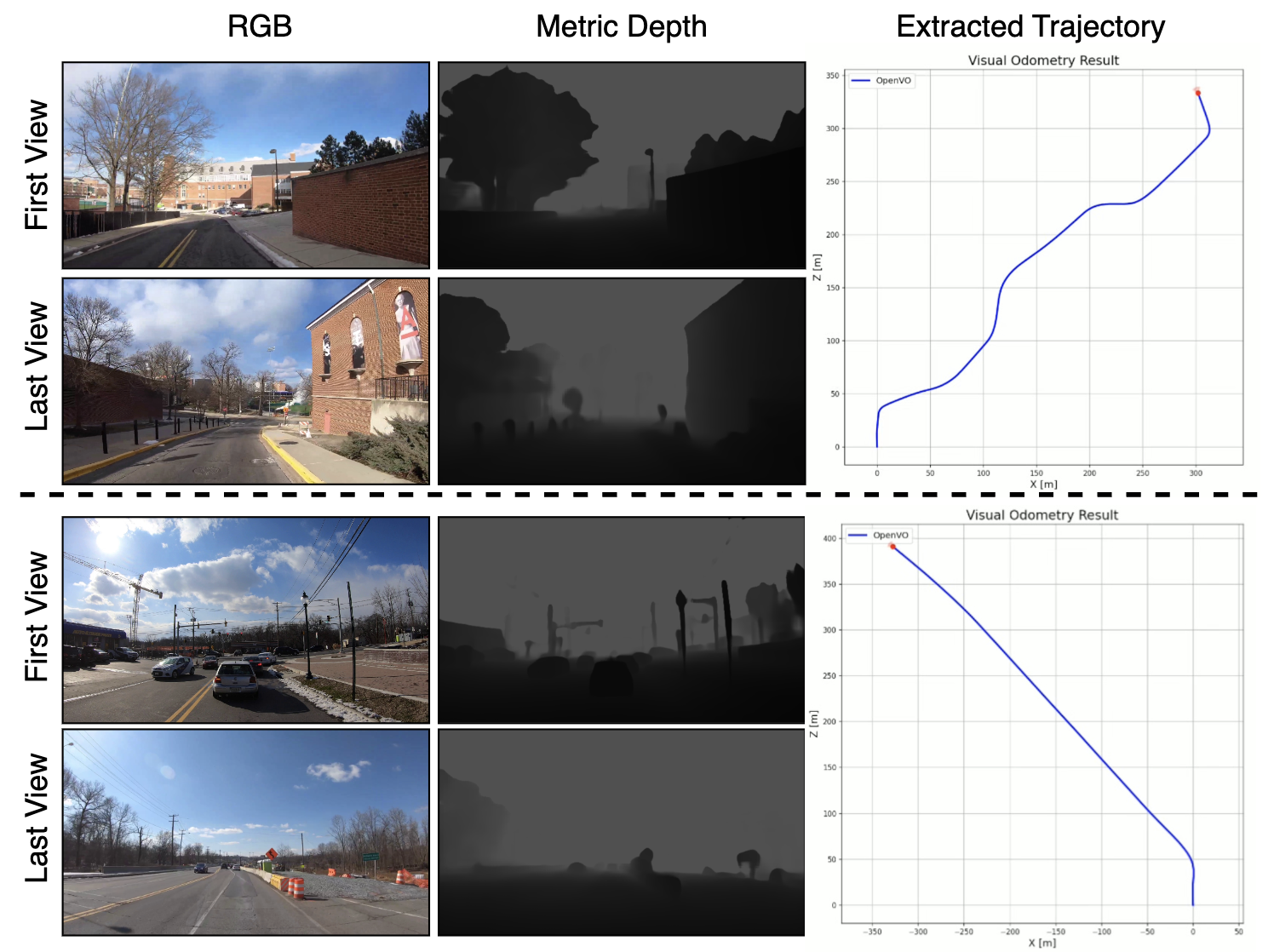
Qualitative results on real-world captured videos. We present two examples, each accompanied by the corresponding RGB frames and reference metric-depth images. Real-world videos commonly exhibit numerous environmental artifacts—such as noise, clutter, and dynamic elements—which pose significant challenges for generalizability and real-world performance assessment. Below is the reference region for the first example
The reference region for the first example.
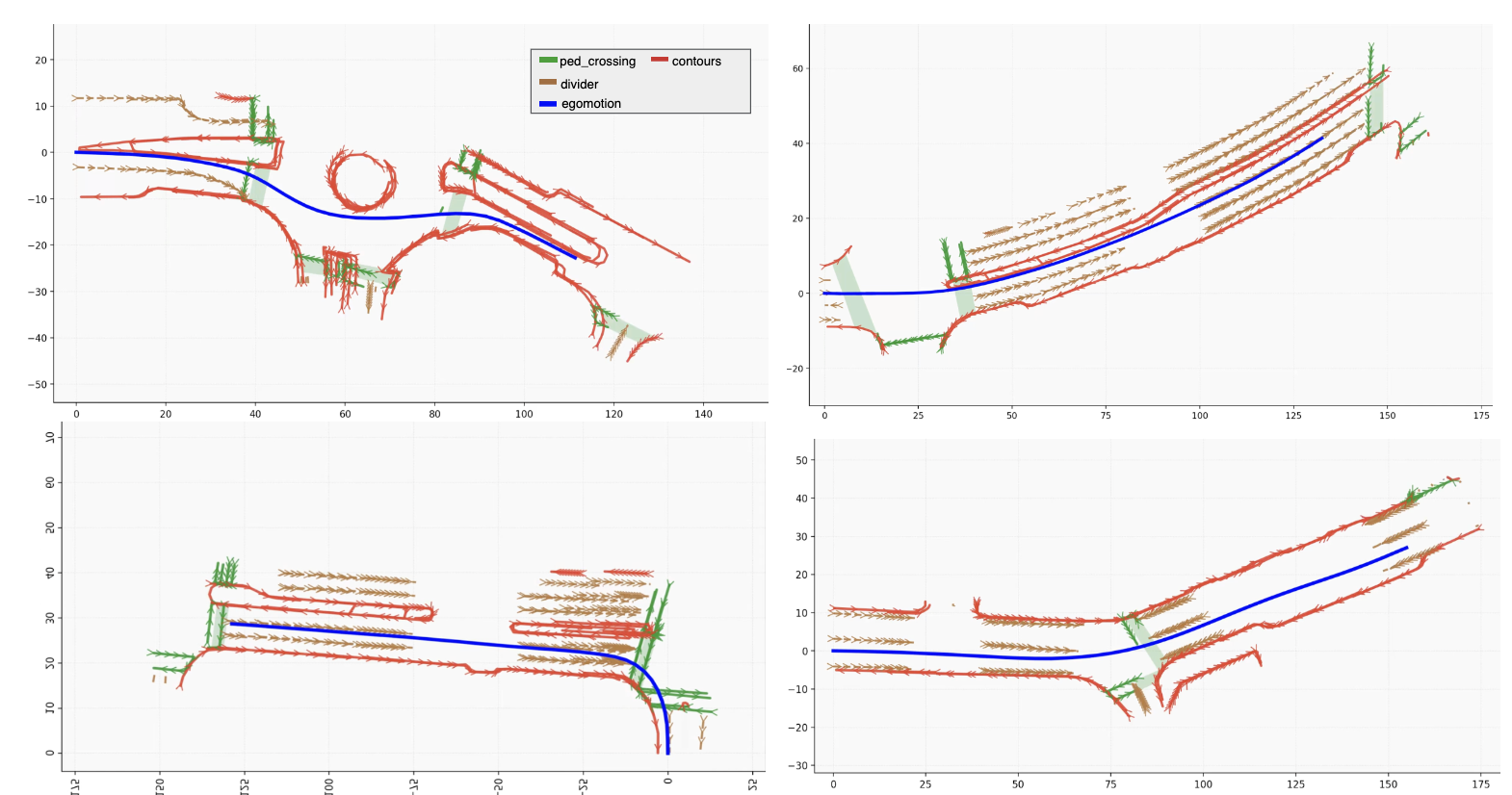
Qualitative results of Global HDMap reconstruction results produced by OpenVO + modified monocular VectorMapNet. Local mapping outputs are gradually fused through OpenVO’s ego-to-world pose estimates, producing a coherent global HD-map reconstruction of the full scenario. We would like to refer to our papers for further details of the OpenVO-enabled monocular-based global map reconstruction.